Biological safety hood
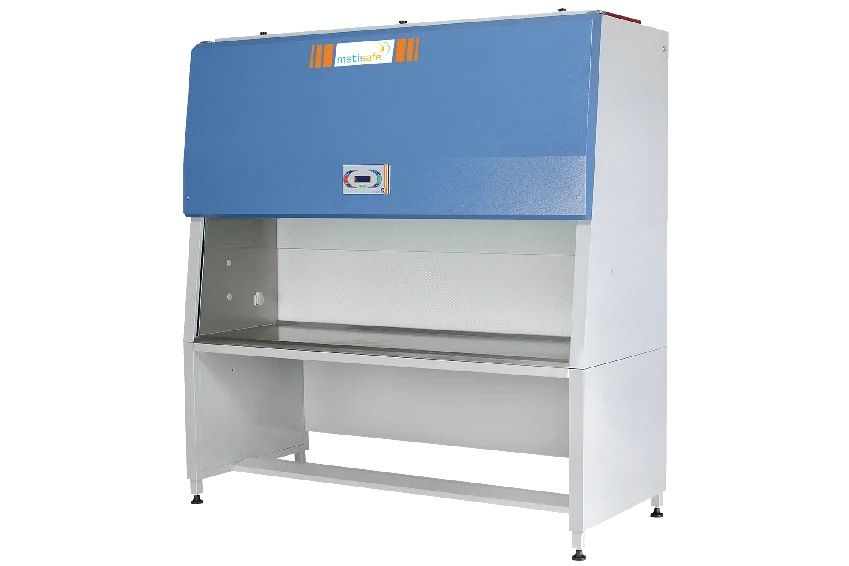

Safety Biology Hood
This device is used to control microbial suspended particles or airborne toxicants as a result of activities such as mixing, centrifuging, pumping and opening in vacuum containers. Biological Safety Cabinets Biology protects the user, the environment and the sample (Manipulated Sample) from the air. The other words of this device are (Laminar Flow Cabinets) and ((Hood of Safety)).
Picture of a safety biology hood
Figure 19. Hood Biological Safety
System usage cases
Safety biology hood is applicable to:
1. Protecting the user against the dangers of infectious agents.
2.Follow the test sample from the contamination.
3. Environmental protection.
These hoods are also used for daily routine work on patches (parasites, bacteria, viruses and mushrooms), cell culture media and under very precise conditions for toxic substances.
Principles of Functional Safety Hygiene
Biological hoods from a cabinet are usually made of steel, a window with a height-adjustable front window, an electric motor ventilation system, an air vent and a set of channels that create a negative pressure in the cabinet. This system generates a layer of air to protect the user from the inside out. Inside the cabin, air passes through a series of channels to high efficiency filters (HEPA) (High Efficiency Particulate Air). Due to the design of the cabinets, the air inside the laboratory is recycled in various ways. The airflow that moves from the filter to the work surface in class II hoods is layered and quiet. A summary of the types of hoods and their specifications are presented in the next section.
A summary of all types of safety hygiene products
Hood type with image
Class I – Type A:
Specifications:
Features: user and environment protection
Air velocity when entering the hood: 38 cm / s (cm / s).
Suitable for working with Risk Factors Level 1, 2, and 3.
High-performance ventilation system, exhaust system that may or may not be external to the outside.
Disadvantages: The contamination barrier of the tested specimen is not in the cabinet.
Class II – Type A:
Specifications:
Features: user protection, sample and environment.
Air velocity during entry into the hood: 38 cm / s (cm / s).
Suitable for working with Risk Factors Level 1, 2, and 3.
Ventilation System: Two high efficiency filters, one mounted on the hood surface, the second filter is installed in the outlet system that may be connected to the outside.
These models recover 70% of the air volume and replace the remaining 30%.
Class II – Type B1:
Specifications:
Features: user protection, sample and environment.
Air velocity when entering the hood: 8/50 cm / s (cm / s).
Suitable for working with Risk Factors Level 1, 2, and 3.
Ventilation System: Two high-efficiency filters recycle contaminated air (70%) into the hood, and is then driven outward after filtering through the front grid (30%).
All biology hoods have a negative pressure.
Possibility to work with low levels of toxic and radioactive substances.
Class II – Type B2:
Specifications:
Features: user protection, sample and environment.
Air velocity during entry into the hood: 8/50 cm / s (cm / s).
Suitable for working with Risk Factors Level 1, 2, and 3.
Ventilation System: There are two high-performance filters for air conditioning and there is no recycling.
There is a negative pressure on all contaminated channels.
It has an outlet channel that allows for work with toxic and radioactive materials.
مطالب مرتبط
What is an autoclave?

The role of liquid nitrogen in the food industry









دیدگاهتان را بنویسید